A diaphragm pump is a versatile piece of equipment widely used in various industries. Its design allows for efficient fluid movement through a simple mechanism. Understanding how a diaphragm pump operates can enhance its application.
The diaphragm pump uses a flexible diaphragm that creates a vacuum to draw fluid in. This action is critical in processes where precise fluid transfer is required. However, its effectiveness can vary based on the medium being pumped. Users must consider factors like viscosity and chemical compatibility.
While diaphragm pumps are reliable, they can face challenges. Issues like diaphragm wear or improper maintenance can hinder performance. Therefore, regular inspection and thoughtful operation are essential for optimal results. Embracing these details can lead to better efficiency and reduced downtime.
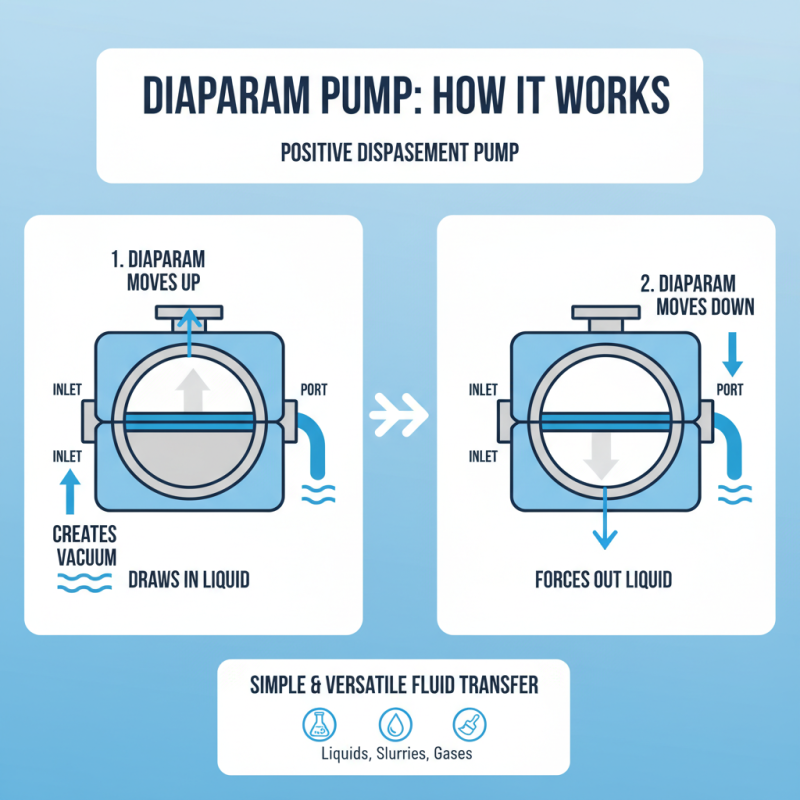
A diaphragm pump is a type of positive displacement pump. It uses a flexible diaphragm to move fluids. The diaphragm’s movement creates a vacuum that draws in liquid. When the diaphragm retracts, it forces the liquid out through a discharge port. This simple mechanism makes diaphragm pumps versatile.
These pumps can handle various fluids, including corrosive substances. They are often found in industrial and agricultural settings. The ability to manage thick slurries is a significant advantage. However, diaphragm pumps can sometimes require frequent maintenance. Over time, the diaphragm may wear out, leading to leaks. Regular inspections are necessary to ensure efficiency.
While diaphragm pumps offer many benefits, they also have limitations. They can be less efficient at high flow rates. Plus, their pulsating flow may not suit all applications. Considering these factors is essential when choosing a pump for specific tasks.
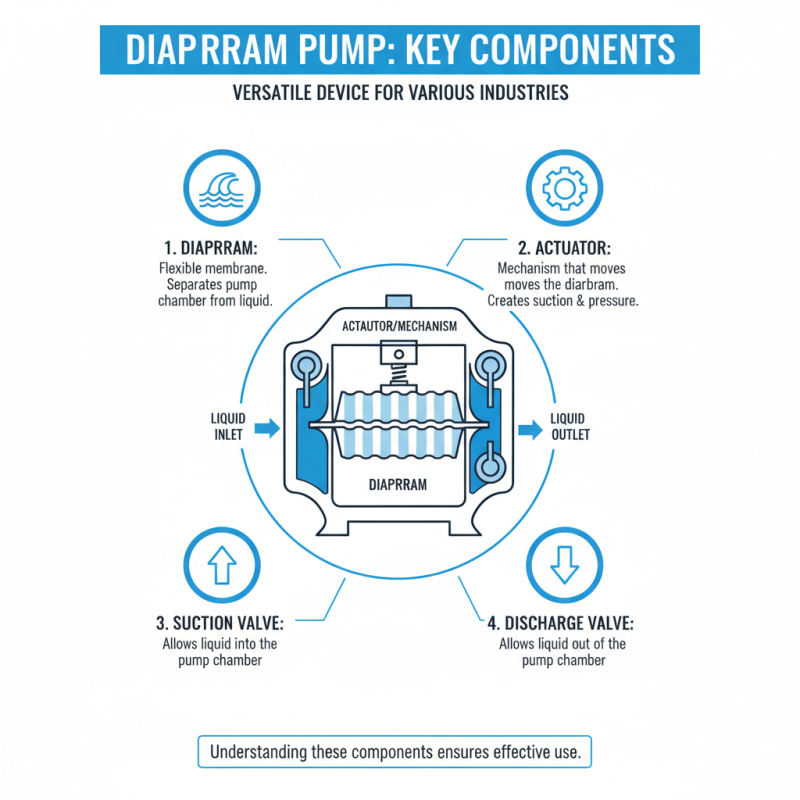
A diaphragm pump is a versatile device used in various industries. Understanding its key components is crucial for effective use. At the heart of the diaphragm pump is the diaphragm itself. This flexible membrane separates the pump chamber from the liquid being moved. When the diaphragm shifts, it creates suction and pressure.
Another vital component is the inlet and outlet valves. These valves control the flow of fluid in and out of the pump. They must work correctly to prevent backflow. Any malfunction can lead to leaks. Users often overlook these parts. Regular checks can ensure they are functioning properly.
Lastly, the air chamber plays an essential role. It helps maintain the balance of the diaphragm’s movements. If the air chamber is not set correctly, the pump may not work efficiently. This might lead to performance issues. It's a reminder that even small components can have a significant impact on overall operation. Each piece should be given attention and care.
Diaphragm pumps are versatile devices widely used for transferring liquids and gases. They consist of a flexible diaphragm that moves back and forth. This motion creates a vacuum, drawing fluid into the pump chamber, then expels it through a discharge outlet. According to a recent market study, diaphragm pumps are projected to witness a CAGR of over 5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to their efficiency in various applications, including chemical processing and food production.
One key aspect of diaphragm pump operation is their ability to handle a variety of fluids. They can manage viscous liquids and even slurries without damage. This makes them an attractive choice for many industries. However, improper installation can lead to cavitation, which may cause damage or operational inefficiencies. Regular maintenance is essential to avoid these flaws and ensure optimal performance.
Tip: Always check the diaphragm for wear and tear. Replace it promptly to maintain pump efficiency. Additionally, keep an eye on the discharge pressure. Abnormal readings could indicate potential issues that need addressing. Maintaining a clean environment can also prevent contamination and prolong pump life.
Diaphragm pumps are versatile equipment widely used in various industries. They offer significant advantages that make them a popular choice for fluid transfer. One major benefit is their ability to handle a wide range of fluids, including viscous, corrosive, and even abrasive materials. This versatility makes them ideal for tasks where traditional pumps might fail.
Their design typically includes two diaphragms, which create a suction and discharge effect. This design minimizes leakage, making diaphragm pumps an excellent choice for sensitive or hazardous fluids. They also operate without the need for lubrication, reducing maintenance efforts.
Tips: Regularly inspect diaphragm pumps for wear and tear. A small crack can lead to major inefficiencies. Also, consider the viscosity of your fluid. Pumps may struggle with thicker liquids.
Another key advantage is their self-priming capability. They can draw fluid without needing to be submerged, which saves time during setup. However, users should note that they might not be suitable for very low-flow applications. Understanding your specific needs is critical for optimal performance.
Tips: If you're working with varied fluid types, have a backup diaphragm ready. This can save you during unexpected down-times.
Diaphragm pumps are versatile tools found in various industries. These pumps use a flexible diaphragm to move fluids. Their design allows for both low and high viscosity fluids. This makes them suitable for diverse applications. They are often used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment.
In food processing, diaphragm pumps handle delicate ingredients. They ensure a smooth and safe transfer without contamination. In pharmaceuticals, these pumps can accurately deliver precise dosages. This precision is crucial in drug manufacturing. However, they may require regular maintenance to prevent failure.
In wastewater treatment, diaphragm pumps manage sludge with ease. But they sometimes struggle with larger solids. This can lead to clogging issues. Awareness of these limitations is essential for operators. Understanding the specific needs of each application can enhance the effectiveness of diaphragm pumps.