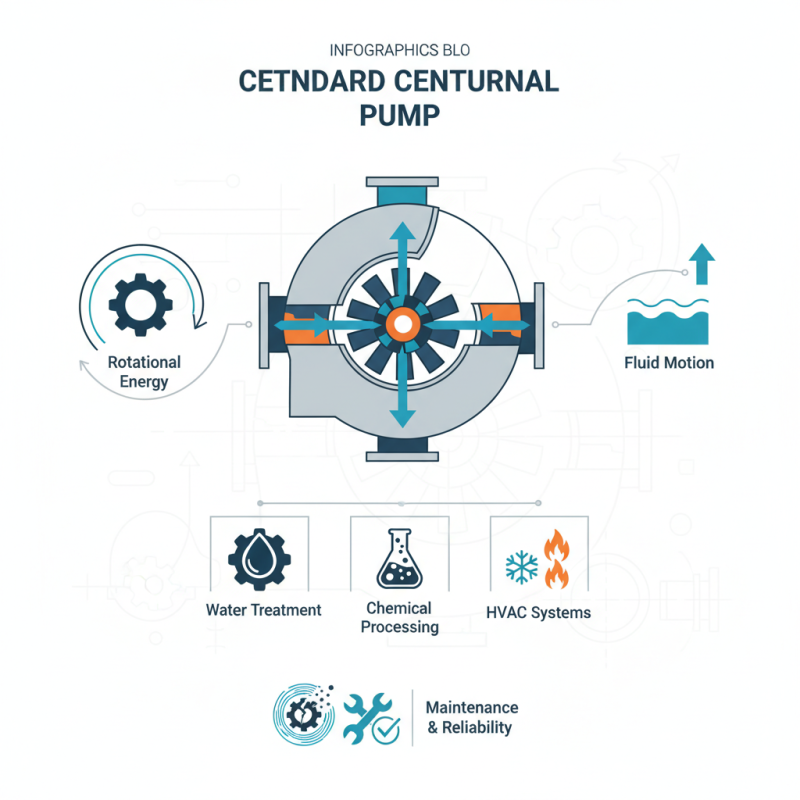
A Standard Centrifugal Pump is a crucial component in various industrial applications. It operates by converting rotational energy into fluid motion. These pumps are widely used in water treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
Understanding how a Standard Centrifugal Pump works is essential for efficient system design. The basic principle involves impellers and volute casings. As the impeller spins, it accelerates the fluid outward. This movement generates pressure, allowing the liquid to flow through the system.
However, not all pumps function perfectly. Issues such as cavitation and wear can affect performance. It’s vital to monitor these factors closely. Over time, pumps may require maintenance or replacement. Proper understanding of the Standard Centrifugal Pump can lead to better efficiency and reliability.
A standard centrifugal pump is a mechanical device designed to move fluids. It operates using a rotating impeller, which imparts kinetic energy to the liquid. This mechanism allows liquids to flow through pipes efficiently. In industrial settings, centrifugal pumps are ubiquitous. According to recent market research, nearly 70% of all pumps used globally are centrifugal pumps.
These pumps are versatile and can handle a variety of fluids. They work best with water and other low-viscosity liquids. Often, they are chosen for their efficiency in moving large volumes. However, challenges can arise, particularly with viscous or corrosive fluids. The pump may struggle to achieve optimal flow rates. Reports suggest that improper selection of pump types can lead to up to 15% inefficiency in operations.
Centrifugal pumps can also experience issues with cavitation. This occurs when vapor bubbles form in low-pressure areas. When these bubbles collapse, they can cause significant damage to the pump. Awareness of this phenomenon is crucial for operators. A thorough understanding of pump operation can mitigate risks and enhance performance. Consistent maintenance and monitoring are essential. Ignoring these factors can lead to increased downtime and repair costs.
Centrifugal pumps are essential in many industries. They convert mechanical energy into hydraulic energy to move fluids. Several components work together seamlessly to achieve this task.
The impeller is a key part. It spins rapidly, creating a vacuum. This pulls fluid into the pump. The volute casing surrounds the impeller. It collects and directs the fluid out. This design helps maintain efficient flow.
Another critical component is the seal. It prevents leaks and maintains pressure within the pump. Over time, seals can wear out. Regular maintenance is vital. Bearings support the rotating shaft and minimize friction. However, they can also fail, leading to inefficiencies. Ensuring these parts work correctly is crucial for optimal performance.
This bar chart displays the efficiency of different standard centrifugal pumps. Efficiency is crucial for minimizing energy consumption and enhancing operational performance in various applications. The values indicate the percentage of energy converted into flow work by each pump.
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in various industries, from water treatment to oil refining. Their operating principle relies on centrifugal force. Essentially, when the pump impeller spins, it generates velocity. This velocity converts into pressure, moving the fluid through the pump and into the piping system.
The impeller design is crucial. It typically consists of curved blades that help in accelerating the fluid. According to a report by the Hydraulic Institute, centrifugal pumps account for 80% of the global market for pumps. This highlights their efficiency and versatility. However, an improper application or design can lead to performance issues, such as cavitation. Understanding the fluid properties is essential to avoid this.
Tips: Regular maintenance is vital. Inspecting the impeller for wear can significantly enhance performance. Additionally, ensure that the pump operates within its design parameters. Running it outside these limits can cause damage.
Fluid viscosity impacts pump efficiency. Higher viscosity fluids require more energy to move. Therefore, choosing the right pump for the specific application is critical. Misjudgments here often lead to inefficiencies and increased operational costs. Examine specifications closely.
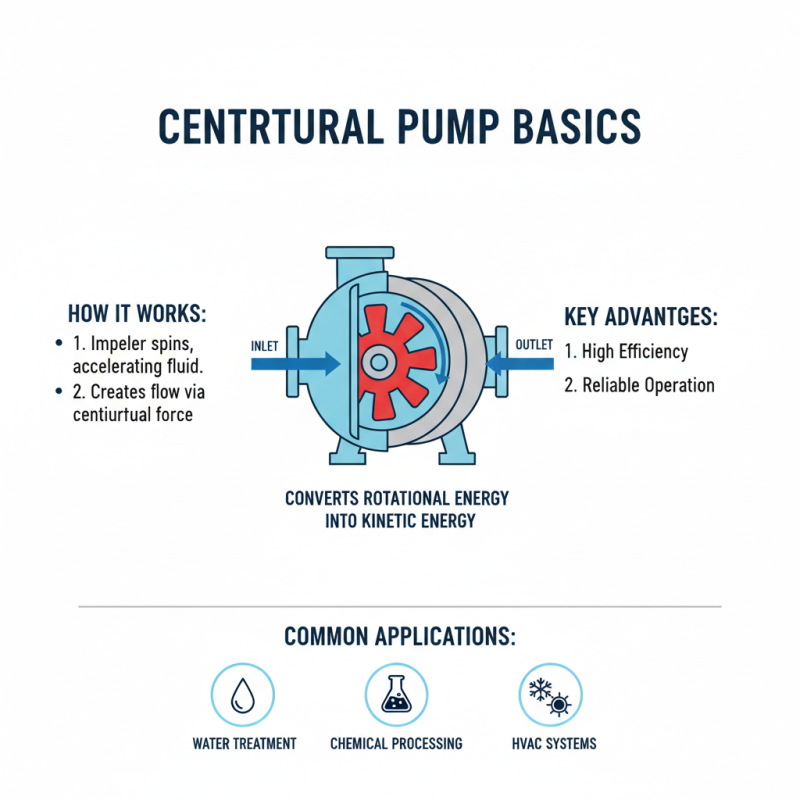
Centrifugal pumps are widely used in various industries due to their efficiency and reliability. They work by converting rotational energy into kinetic energy. This process creates a flow of fluid through a series of impellers. Common applications include water treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC systems.
In water treatment plants, centrifugal pumps help in moving water through filtration systems. They are vital in maintaining consistent water supply. In chemical processing, these pumps handle corrosive and viscous fluids. This requires careful material selection to ensure durability. HVAC systems rely on centrifugal pumps for circulation of coolant and air.
However, reliance on these pumps isn't without challenges. They can face issues like cavitation, which reduces efficiency. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent breakdowns and ensure optimal performance. Users must always monitor performance and be ready for adjustments. Understanding every aspect takes time and knowledge, often leading to pitfalls.
Centrifugal pumps are widely used for various applications. They are efficient at moving fluids. However, like any technology, they come with their benefits and limitations. The main advantage of centrifugal pumps is their ability to handle large volumes of liquid. They operate continuously and can be throttled easily. This makes them ideal for systems requiring constant flow.
On the downside, centrifugal pumps are not always ideal for high viscosity liquids. They struggle with thick fluids, which can lead to inefficiencies. Additionally, they can lose prime under certain conditions. This can be problematic in critical processes. A significant limitation is their sensitivity to changes in pressure and flow. Such factors can negatively impact performance, leading to potential disruption.
Users must evaluate the specific needs of their systems. Sometimes, a centrifugal pump is not the best fit for the job. It's essential to be mindful of these drawbacks. Addressing them may require additional equipment or modifications. In some cases, a different pump type might be more suitable. This reflection can lead to more robust and effective fluid handling solutions.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Centrifugal Pump |
| Operating Principle | Uses rotational energy to move fluid |
| Applications | Water supply, irrigation, chemical processing |
| Efficiency | High efficiency at a constant flow rate |
| Advantages | Simple design, low maintenance, versatile |
| Limitations | Not effective for high-viscosity fluids, limited self-priming ability |
| Common Materials | Stainless steel, cast iron, plastic |
| Maintenance Requirements | Regular checks, seal and bearing replacement |